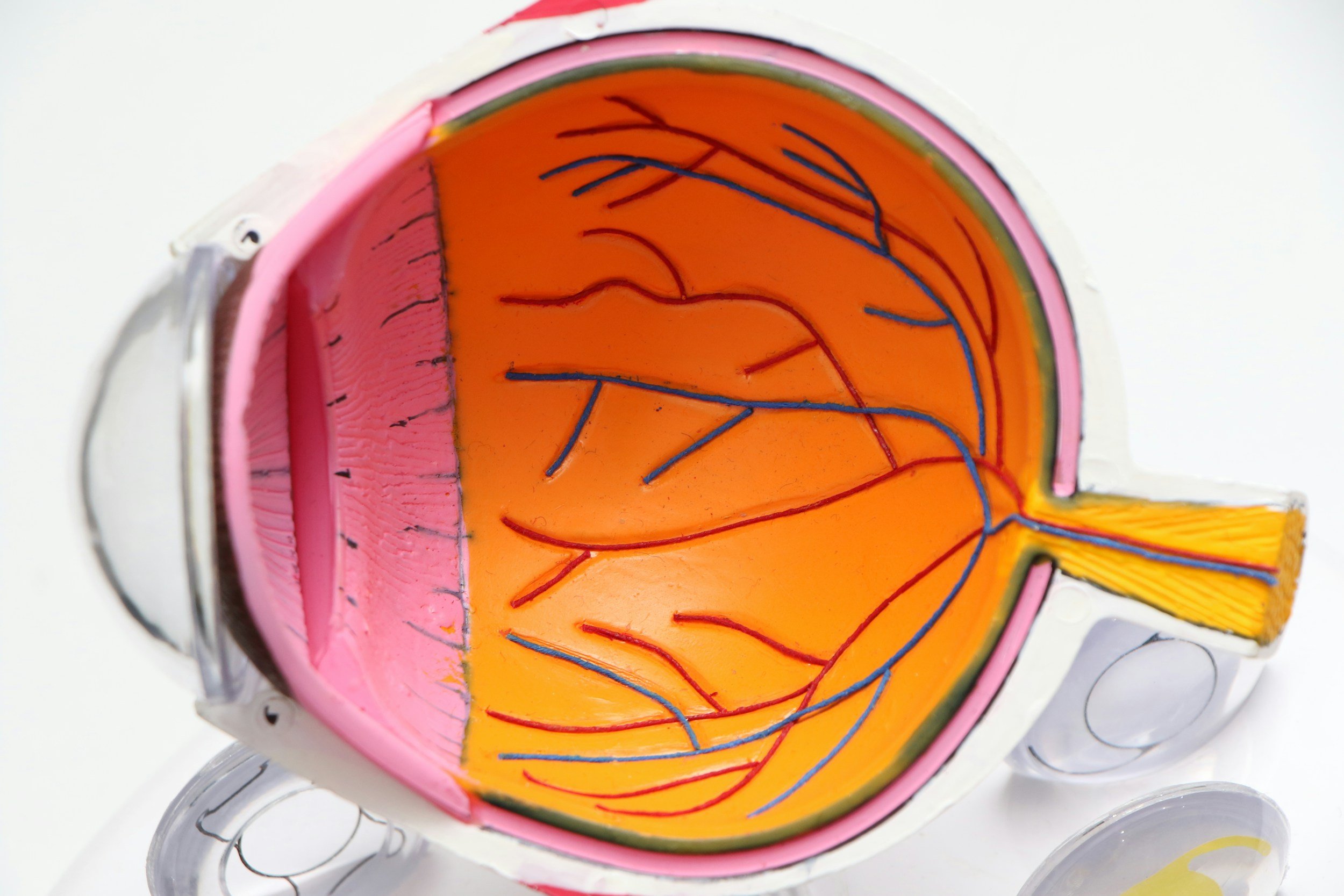
What is cranial nerve 7?
Cranial Nerve 7, also known as the Facial Nerve, is one of the twelve cranial nerves in the peripheral nervous system. It is responsible for controlling the muscles of facial expression, as well as the sensation of taste on the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. Additionally, Cranial Nerve 7 plays a crucial role in tear production, salivation, and transmitting taste sensations from the taste buds to the brain.
What is cranial nerve 6?
Cranial Nerve 6, also known as the abducens nerve, is one of the 12 cranial nerves in the human nervous system. This nerve controls the lateral rectus muscle, which is responsible for the outward movement of the eye. Cranial Nerve 6 originates from the pons in the brainstem and plays a crucial role in maintaining proper eye movement and coordination.
What is cranial nerve 5?
Cranial Nerve 5, also known as the Trigeminal Nerve, is one of the twelve cranial nerves in the head. It is the largest of all the cranial nerves and is responsible for providing sensory innervation to the face and motor functions for chewing. The Trigeminal Nerve has three main branches: the ophthalmic branch, the maxillary branch, and the mandibular branch.
What is cranial nerve 4?
Cranial Nerve IV, also known as the Trochlear Nerve, is the fourth of the 12 cranial nerves. This nerve is responsible for the motor function of the superior oblique muscle, which is one of the extraocular muscles that control eye movement. The trochlear nerve aids in moving the eye downward and laterally.
Given its role in eye movement, any issues with the trochlear nerve can lead to symptoms such as double vision (diplopia) and difficulty moving the affected eye in certain directions.
What is cranial nerve 3?
Cranial nerve 3, also known as the oculomotor nerve, is one of the 12 cranial nerves emerging directly from the brain. It plays a crucial role in controlling the movements of most of the muscles in the eye, including the constriction of the pupil and the ability to move the eye in different directions. This nerve also contributes to the regulation of the eyelid's position and certain reflex actions related to vision. Dysfunction of the oculomotor nerve can lead to various vision problems, such as double vision, drooping eyelids, and uncontrolled eye movements, which may require medical intervention and attention.
What is cranial nerve 2?
Cranial Nerve 2, also known as the Optic Nerve, plays a critical role in vision. It carries visual information from the retina of the eye to the brain for processing. This nerve is responsible for transmitting signals related to light, colors, shapes, and movement from the eye to the brain's visual centers. Any damage or impairment to Cranial Nerve 2 can result in various visual disturbances, including partial or complete vision loss. It is crucial for maintaining the sense of sight and coordinating proper visual perception.
What is cranial nerve 1?
Cranial nerve I, also known as the olfactory nerve, is responsible for the sense of smell in the human body. It transmits information from the nasal cavity to the brain, allowing individuals to detect and differentiate various odors. The olfactory nerve plays a vital role in our perception of the environment and can trigger emotional responses and memories through olfactory sensations.
Rheumatoid Arthritis and Chiropractic Care
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune condition that primarily affects the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and stiffness. This condition occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own tissues, specifically the synovium – the lining of the joints.
The Chiropractic approach to Carpal Tunnel
It is estimated upon clinical examination that 3.8% of the population suffers from CTS within the general population. CTS is highly related to occupations that require repetitive use of the upper extremity and neck. Factory operators, fabricators, laborers as well as tech support, administrative assistants, and salespersons, are among the most effected by CTS.